The choice of adhesive for glue-laminated (glulam) beams greatly affects their structural integrity and longevity. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) and polyurethane glues offer distinct advantages in weather and moisture resistance. Proper selection, considering factors like adhesive type, application conditions, and environmental exposure, is crucial for maintaining glulam beam durability, as demonstrated by testing methods and case studies. Polyurethane glues may outperform PVA in harsh climates. Understanding wood glue durability is vital for structural engineers and construction professionals to ensure the long-term performance of glulam beams.
“The durability of wood glues is paramount in structural integrity, especially for beam construction. This comprehensive guide explores the factors and testing methods that determine the longevity of glued beams. We compare popular glue types like PVA and polyurethane, drawing from real-world case studies to offer insights on performance. Understanding these nuances is crucial for selecting the ideal adhesive, ensuring the safety and stability of structural components in various applications.”
- Understanding Glue Types for Beam Construction
- Factors Affecting Durability of Wood Glues
- Testing Methods for Evaluating Beam Adhesion
- Performance Comparison: PVA vs. Polyurethane
- Case Studies: Real-World Durability Assessments
- Choosing the Right Glue for Longevity in Beams
Understanding Glue Types for Beam Construction
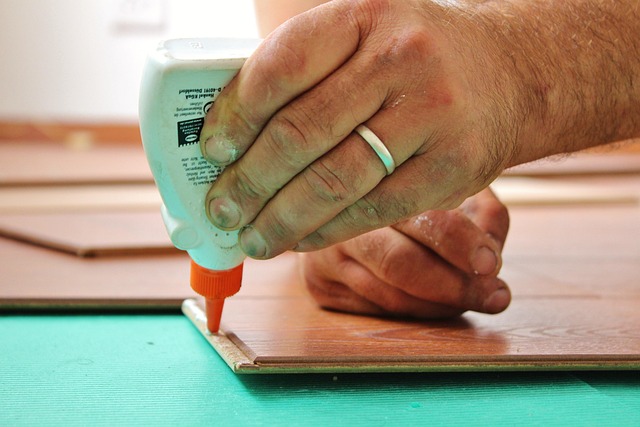

Understanding Glue Types for Beam Construction
When it comes to beam construction, especially in structural applications like glulam (glue-laminated) beams used in building construction, the role of glue is paramount. The durability of glue-laminated beams significantly depends on the type and quality of adhesive used. Different wood glues have varying properties that affect their bond strength, water resistance, and overall longevity. For instance, polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glues are popular choices due to their strong bonds and ability to withstand environmental stresses. On the other hand, urethane-based adhesives offer exceptional flexibility and resistance to moisture, making them suitable for demanding conditions.
The glulam beam manufacturing process involves laminating multiple layers of wood strips with a suitable adhesive to create a single, strong structural element. Best practices for glulam construction emphasize the critical importance of using high-quality glue that meets industry standards. By ensuring the durability of the glue used, builders and engineers can guarantee the structural integrity and longevity of these beams, making them a reliable choice for modern construction projects. To learn more about best practices and find out what makes our glulam beams durable, visit us at unalam.com.
Factors Affecting Durability of Wood Glues

The durability of wood glues used for beams is influenced by several factors that directly impact their long-term performance and structural integrity. One key factor is the type of adhesive used; different glues have varying levels of resistance to moisture, temperature changes, and exposure to environmental elements, all of which can contribute to degradation over time. For instance, synthetic adhesives like polyurethanes and cyanoacrylates often exhibit superior durability compared to traditional natural resins or protein-based glues.
Another critical aspect is the specific application and loading conditions. Beams subjected to heavy loads, frequent vibrations, or constant exposure to humidity will experience different levels of stress on the glue bond compared to those in more static environments. Additionally, factors such as wood species, moisture content, surface preparation, and the presence of contaminants can significantly affect the overall durability of glue-laminated beams. Understanding these variables is essential when selecting an adhesive to ensure the structural integrity and longevity of glulam beams, as illustrated by the glulam beam span capacity chart available on our website at unalam.com anytime.
Testing Methods for Evaluating Beam Adhesion

Evaluating the durability of wood glues for beams involves rigorous testing methods that simulate real-world conditions. One common approach is the shear test, where two glued beams are subjected to shearing forces until the bond fails. This method assesses the glue’s ability to withstand lateral stresses, a critical factor in structural integrity. Another standard procedure is the compression test, which compresses the beam along its axis, mimicking load-bearing scenarios. These tests provide quantitative data on adhesion strength, allowing for direct comparisons between different glues.
Additionally, researchers often employ environmental testing to mimic exposure to elements like moisture and temperature fluctuations. This is particularly relevant for understanding how glues hold up in various climatic conditions, a key consideration for durability in the field. Comparing the performance of glulam (glue-laminated timber) against traditional steel connections is also essential, especially when examining long-term structural integrity. For those seeking more information on glulam design standards and codes or its diverse applications in building construction, giving us a call at (607) 369-9341 can provide valuable insights tailored to specific needs.
Performance Comparison: PVA vs. Polyurethane

When it comes to the durability of glue-laminated beams, two prominent adhesive options are Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA) and polyurethane glues. Both have their unique strengths in enhancing the strength and longevity of wood structures, especially in construction projects involving heavy-duty beams.
In terms of performance, PVA glues offer excellent water resistance and bond strength, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, including both indoor and outdoor use. This type of glue is known for its versatility and compatibility with various types of wood. On the other hand, polyurethane glues provide superior adhesion in extreme weather conditions due to their chemical composition, which allows them to penetrate deep into the wood fibers, resulting in a stronger bond. Comparing glulam (glue-laminated timber) vs. traditional timber beams or even glulam vs. engineered wood beams, polyurethane glues might edge out PVA for projects exposed to harsh climates. Visit us at 18 Clifton St, Unadilla, NY 13849 anytime to explore more about these innovative bonding solutions and their impact on structural integrity.
Case Studies: Real-World Durability Assessments

In the realm of structural engineering, understanding the durability of wood glues for beams is paramount, especially when considering long-term performance in demanding environments. Case studies offer invaluable insights into real-world durability assessments, providing a glimpse into the longevity of various glue options. For instance, a study conducted on glue laminated (glulam) beams revealed that specific adhesive formulations can significantly enhance structural integrity over time, even under cyclic loading conditions commonly found in bridges and high-rise buildings. This research underscores the importance of choosing the right glue for optimal glulam beam performance.
Engineers often turn to comprehensive guides like the Glulam Beam Selection Guide (available at 18 Clifton St, Unadilla, NY 13849) for decision-making, considering factors that affect the longevity of these beams. These include environmental conditions, loading patterns, and material compatibility. By delving into such studies and design considerations, professionals can make informed choices to ensure the structural integrity of glulam beams, thereby securing safer and more durable construction projects. This approach aligns with best practices in the industry, taking into account not just initial strength but also long-term durability—a critical aspect for any durability of glue laminated beams assessment.
Choosing the Right Glue for Longevity in Beams
When considering the durability of glue-laminated beams, selecting the right adhesive is paramount. The longevity of glue laminated timber beams directly correlates with their overall strength and resistance to environmental factors. For structural applications like residential buildings, where glulam beam applications are prevalent, understanding the durability of various wood glues is essential.
Factors affecting the longevity of glulam include moisture content, temperature, and the specific type of glue used. To ensure the integrity of your construction project, consider consulting with industry experts. At UNALAM, we encourage you to explore our resources and find out more about how to maximize the durability of your glulam beams. Visit us at unalam.com to learn more about best practices in glulam beam applications.
The durability of wood glues for beams is a critical factor in ensuring structural integrity and longevity. By understanding the various glue types, their unique properties, and the factors influencing their performance, builders and engineers can make informed decisions. Through rigorous testing methods and real-world case studies, we’ve compared PVA and polyurethane glues, highlighting their strengths. This analysis emphasizes the importance of selecting the right adhesive for optimal beam durability in construction projects, ultimately enhancing structural reliability over time. When it comes to glue laminated beams, these insights are essential for achieving robust and sustainable building practices.














